Key Highlights
- Bert, a German Aerospace Center robot, leads space exploration with terrain skills
- Bert, the first leg-based robot controlled from the ISS, advances space exploration
- Robots like Bert and NASA’s Au-Spot boost space exploration with agility and sensors
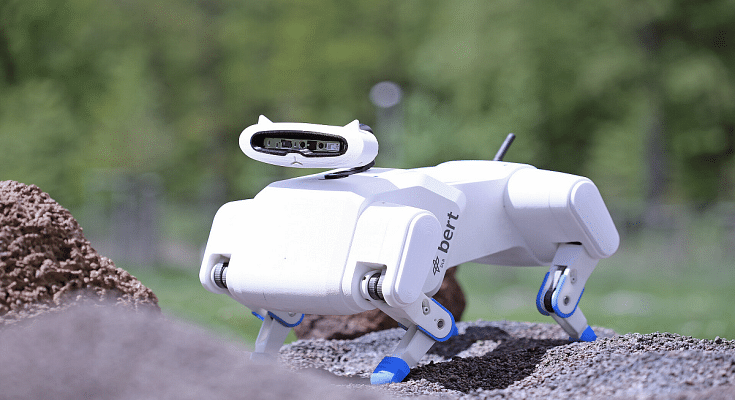
Often addressed as man’s best friend, dogs have long been valued for their loyalty, intelligence, and versatility in various tasks. But what if dogs could extend their assistance beyond Earth’s bounds and aid space exploration? This vision is at the heart of Bert, a four-legged robot developed by the German Aerospace Center (DLR), designed to traverse challenging terrain and assist in remote exploration missions on celestial bodies like the Moon and Mars. Also Read | Xiaomi Showcases A Bio-Inspired Quadruped Robot ‘CyberDog’ In India: Check Out Specs
Bert: The Space Rover
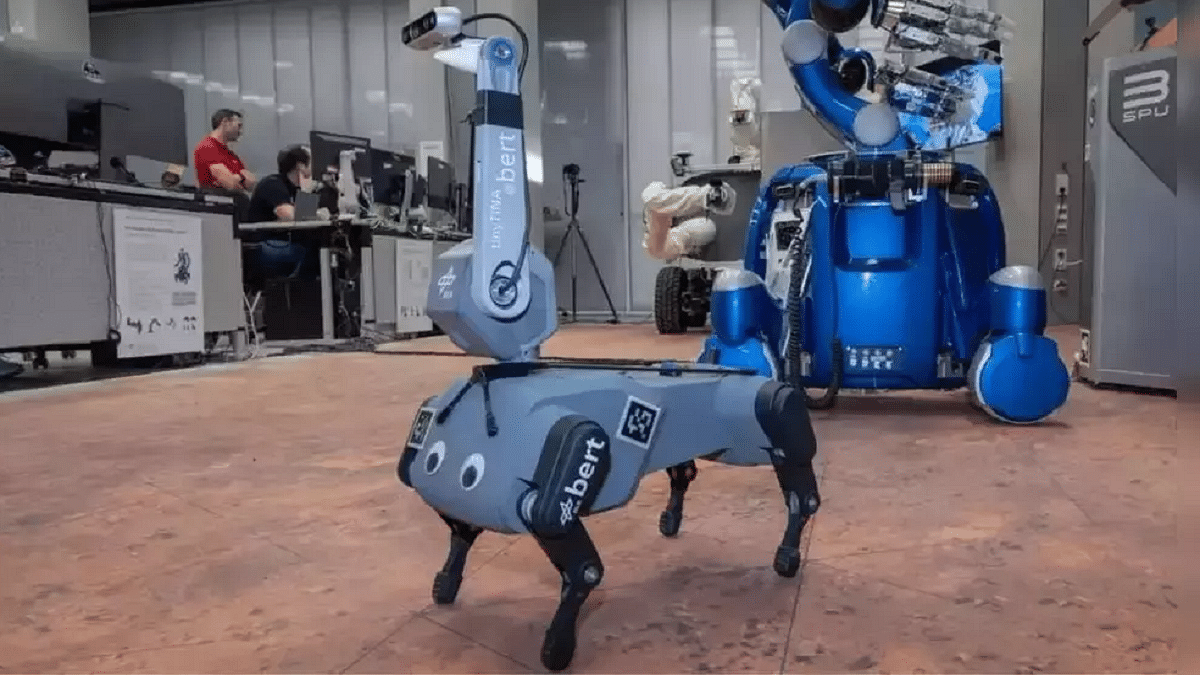
Bert, resembling a canine equipped with advanced capabilities, represents a significant leap in robotic exploration technology. Developed by the DLR, Bert boasts the ability to walk, trot, gallop, and climb, enabling it to navigate rough terrain and access locations inaccessible to conventional robots. As part of the Surface Avatar project, Bert aims to revolutionize remote-controlled robot operations on extraterrestrial surfaces.
A Historic Achievement
In January 2024, Bert achieved a historic milestone by becoming the first leg-based robot to be controlled by an astronaut aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Supervised by Swedish ESA astronaut Marcus Wandt, Bert autonomously explored DLR’s Mars laboratory on Earth, with Wandt directing its movements using a tablet interface. This groundbreaking experiment showcased the potential of telerobotics in facilitating human exploration and work in space.
Telerobotics: Challenges
Telerobotics, essential for future space missions, faces numerous challenges such as communication delays and limited bandwidth. However, projects like the Surface Avatar endeavor to overcome these obstacles through innovative technologies like leg-based locomotion and intelligent autonomy, paving the way for more efficient and immersive remote exploration experiences.
Also Read | Want A Clean Home? Check Our List Of Best Robot Floor Cleaners In India
Beyond Bert: The Au-Spot Project

NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is also spearheading efforts in robotic space exploration with its Au-Spot project. Derived from Boston Dynamics’ Spot robot, Au-Spot boasts advanced sensory capabilities and communication systems, making it a valuable asset for autonomous exploration missions. Part of NASA’s NeBula project, Au-Spot aims to map and explore extreme environments with potential implications for human exploration endeavors.
Robotic Dogs: Pioneers Of Space Exploration
Bert and Au-Spot exemplify the potential of robotic dogs in advancing space exploration. Their agility and adaptability enable them to navigate challenging terrains, complementing the capabilities of human and traditional robotic explorers. As technology continues to evolve, robotic dogs may emerge as indispensable companions in humanity’s quest to unlock the mysteries of the cosmos.
Also Read | Amazon Self-Driving Electric Robotaxi Fares Passengers Successfully In California: New Leap In EV Space?
